Content
No more long story! This post is going to focus on the key difference between deep copy and shallow copy only. I will also give the code to show the difference clearly.
Difference
Shallow copy and deep copy is only cared when you facing complex object data type. The primitive data type such as number, string, boolean, undefined, symbol is not included; Also the simple object type such as objects with primitive data type as values for each key is not included as well.
So we are going to deal with the object that include another object as values of keys.
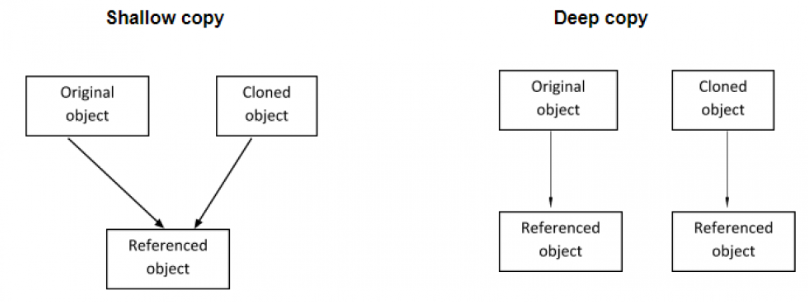
The most significant difference is shallow copy will duplicate the top-level properties, but the nested object is shared with the original(source), whereas deep copy will duplicate every properties include their nested objects. The copy and the original object will not share anything, so it is a copy of the original.
Shallow Copy Code
let obj = {
'name':'John',
'age':28,
'families':[
{
'name':'Alice',
'age':27,
},{
'name':'Bob',
'age':5,
}
]
}
let newObject = shallowCopy(obj)
function shallowCopy(obj){
let output = obj instanceof Array?[]:{}
for (let prop in obj){
// This is to ensure the prop is from obj not from obj's prototype
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(prop)){
output[prop]=obj[prop]
}
}
return output
}
console.log('newObj',newObject)//The new object from shallow copy
/* The new object from shallow copy
{
name: "John"
age: 28,
families: [
{
name: "Alice",
age: 27
},
{
name: "Bob",
age: 5
}
],
}
*/
newObject.families[0].name = 'Sara'//Change properties of the new object
console.log('ori obj',obj)//The original obj
/* The original obj
{
name: "John"
age: 28,
families: [
{
name: "Sara",
age: 27
},
{
name: "Bob",
age: 5
}
],
}
*/
From above, when the properity of new object from shallow copy change, the original object still get effected. The new object and original object still have connection after shallow copy.
Deep Copy Code
let obj = {
'name':'John',
'age':28,
'families':[
{
'name':'Alice',
'age':27,
},{
'name':'Bob',
'age':5,
}
]
}
let newObject = DeepCopy(obj)
function DeepCopy(obj){
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null){
return obj
}
let output = obj instanceof Array?[]:{}
for (let prop in obj){
// This is to ensure the prop is from obj not from obj's prototype
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(prop)){
// recursively copy the nested object
output[prop]=DeepCopy(obj[prop])
}
}
return output
}
console.log('newObj',newObject)//The new object from shallow copy
/* The new object from shallow copy
{
name: "John"
age: 28,
families: [
{
name: "Alice",
age: 27
},
{
name: "Bob",
age: 5
}
],
}
*/
newObject.families[0].name = 'Sara'//Change properties of the new object
console.log('newObj after change',newObject)//The new object after properity change
/* The original obj
{
name: "John"
age: 28,
families: [
{
name: "Sara",
age: 27
},
{
name: "Bob",
age: 5
}
],
}
*/
console.log('ori obj', obj)//The original obj
/* The original obj
{
name: "John"
age: 28,
families: [
{
name: "Alice",
age: 27
},
{
name: "Bob",
age: 5
}
],
}
*/
From above, when the properity of new object from deep copy change, the original object does not change. The new object and original object have no connection and they are two independent objects now.