141. Linked List Cycle (Python)
Related Topic
Description
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Sample I/O
Example 1
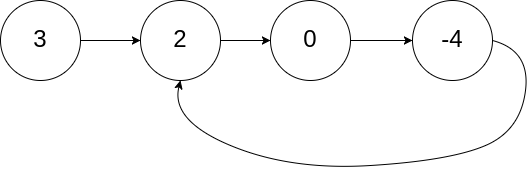
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2
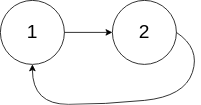
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3

Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Follow Up
Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
Methodology
Set fast and slow pointers on the linked list, fast pointer will move to step each time while the slow pointer will only move 1 step. If there is loop, then fast and slow pointers will finally be coincided.
Code
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
fast, slow = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.next
if fast == slow:
return True
return False
BigO
Iterate the both linked lists once, so total time complexity is O(m+n) where m steps of fast pointer and n is steps of slow pointer