429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal (Python)
Related Topic
Description
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Sample I/O
Example 1
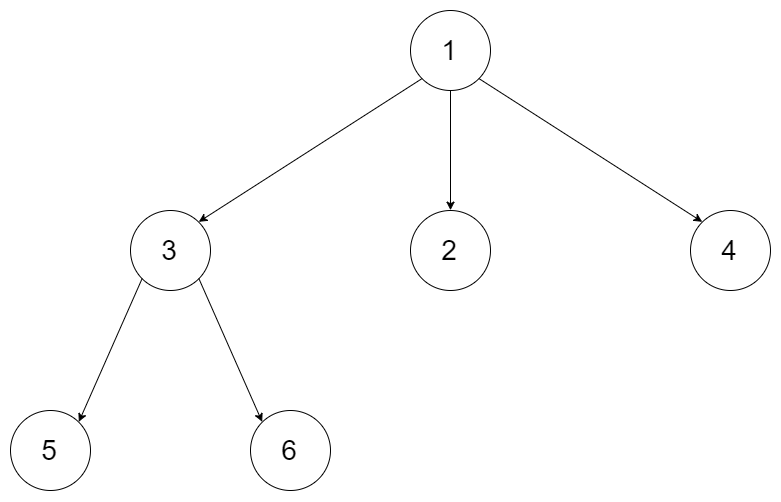
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
Example 2
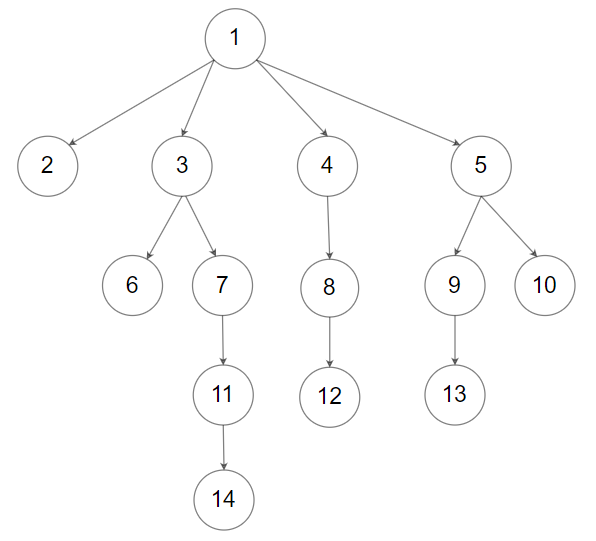
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Note
- The depth of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to 1000.
- The total number of nodes is between [0, 10^4].
Methodology
This question is similart with question 559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree (Python) but this time we are going to get print nodes by level.
We need tmp list to append each level node’s then append the tmp list to final result list.
Code (BFS)
def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:
if not root: return []
q = collections.deque([root])
res = []
while q:
temp = []
size = len(q)
for i in range(size):
node = q.popleft()
temp.append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
q.append(child)
res.append(temp)
return res
BigO
We traversal all elements of tree once so total time complexity is O(n) where is the size of the tree