1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix (Python)
Related Topic
Description
In an N by N square grid, each cell is either empty (0) or blocked (1).
A clear path from top-left to bottom-right has length k if and only if it is composed of cells C_1, C_2, …, C_k such that:
- Adjacent cells C_i and C_{i+1} are connected 8-directionally (ie., they are different and share an edge or corner)
- C_1 is at location (0, 0) (ie. has value grid[0][0])
- C_k is at location (N-1, N-1) (ie. has value grid[N-1][N-1])
- If C_i is located at (r, c), then grid[r][c] is empty (ie. grid[r][c] == 0). Return the length of the shortest such clear path from top-left to bottom-right. If such a path does not exist, return -1.
Sample I/O
Example 1
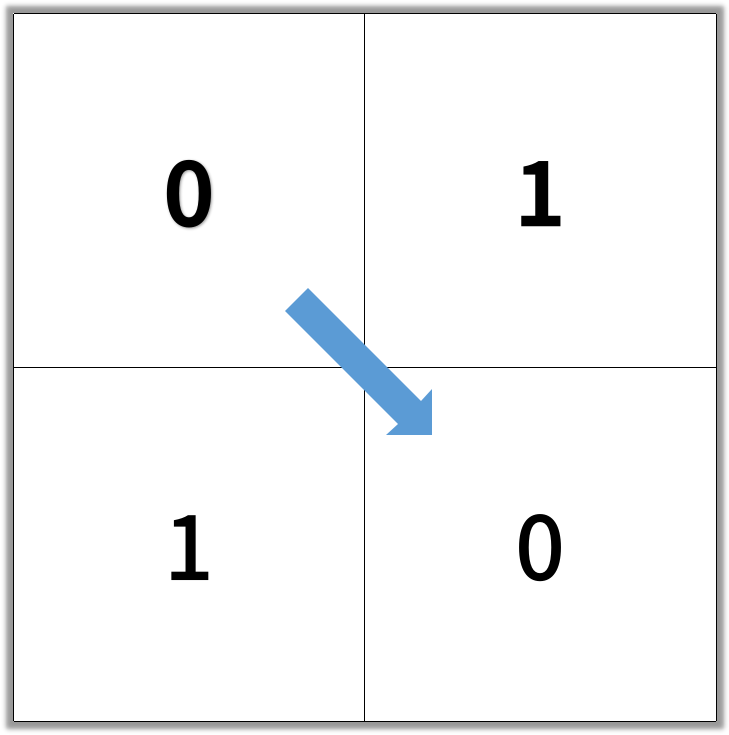
Example 2
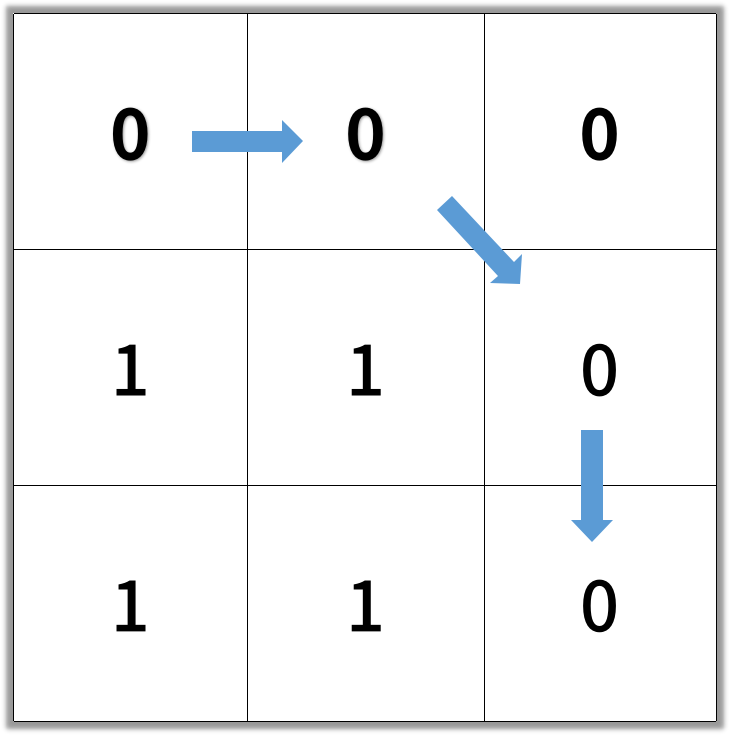
Note
- 1 <= grid.length == grid[0].length <= 100
- grid[r][c] is 0 or 1
Methodology
Append the start path coordinate to queue. Use BFS traversal the 2D list from path coordinate pop out from queue. Each time expand the current path coordinate for 8 directions. And append the 8 directions’s path to queue. The first path to reach bottom right will return the steps.
Code (BFS)
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dirs = [(-1,-1),(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,1),(1,1),(1,0),(1,-1),(0,-1)]
row,col = len(grid),len(grid[0])
if grid[0][0] or grid[-1][-1]:
return -1
if row == 1 and grid[0][0] == 0:
return 1
q = collections.deque()
q.append((0,0))
visited = set()
visited.add((0,0))
step = 1
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
x, y = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x+dx, y+dy
if 0 <= nx< row and 0<= ny < col and grid[nx][ny] == 0 and (nx,ny) not in visited:
visited.add((nx,ny))
q.append((nx,ny))
if nx == row-1 and ny == col-1:
return step + 1
step += 1
return -1
BigO
We traversal all elements of 2D list once so total time complexity is O(mn) where m is the size of row and n is the size of column