994. Rotting Oranges (Python)
Related Topic
Description
In a given grid, each cell can have one of three values:
- the value 0 representing an empty cell;
- the value 1 representing a fresh orange;
- the value 2 representing a rotten orange. Every minute, any fresh orange that is adjacent (4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return -1 instead.
Sample I/O
Example 1
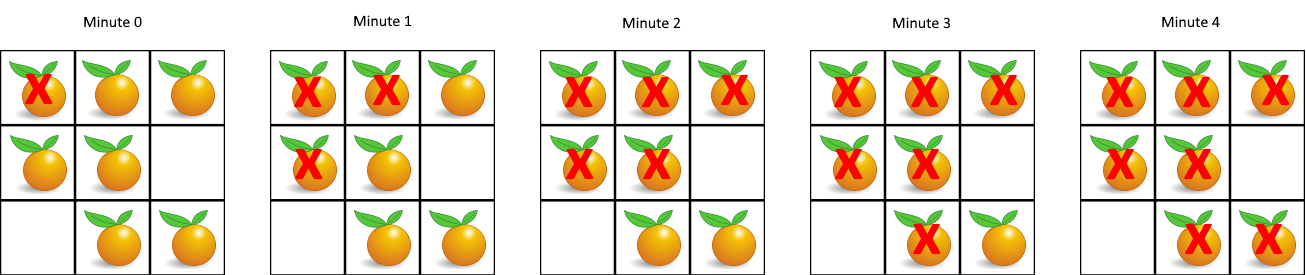
Input: [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
Output: 4
Example 2
Input: [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
Example 3
Input: [[0,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
Note
- 1 <= grid.length <= 10
- 1 <= grid[0].length <= 10
- grid[i][j] is only 0, 1, or 2.
Methodology
- Add all fresh oranges to fresh_set and append all rotten oranges to rotten_queue.
- Use BFS to find all fresh oranges that adjacent to the current rotten orange, turn these fresh oranges to rotten and remove these from fresh_set. In the meantime, track the steps of turning.
- After we finish the turning, if there is still a fresh orange in fresh_set, return -1 otherwist return the step.
Code (BFS)
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row, col = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [(-1,0),(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1)]
fresh_set=set()
rotten = collections.deque()
step = 0
for x in range(row):
for y in range(col):
if grid[x][y]==1:
fresh_set.add((x,y))
elif grid[x][y]==2:
rotten.append([x,y,step])
while rotten:
x,y,step = rotten.popleft()
for dx, dy in dirs:
if 0<=x+dx<row and 0<=y+dy<col and grid[x+dx][y+dy] == 1:
grid[x+dx][y+dy]=2
fresh_set.remove((x+dx,y+dy))
rotten.append([x+dx,y+dy,step+1])
return step if not fresh_set else -1
BigO
We traversal all elements of 2D list once so total time complexity is O(mn) where m is size of row and n is size of columns