743. Network Delay Time (Python)
Related Topic
Description
There are N network nodes, labelled 1 to N.
Given times, a list of travel times as directed edges times[i] = (u, v, w), where u is the source node, v is the target node, and w is the time it takes for a signal to travel from source to target.
Now, we send a signal from a certain node K. How long will it take for all nodes to receive the signal? If it is impossible, return -1.
Sample I/O
Example 1
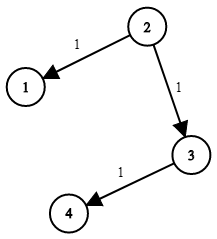
Input: times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], N = 4, K = 2
Output: 2
Note
- N will be in the range [1, 100].
- K will be in the range [1, N].
- The length of times will be in the range [1, 6000].
- All edges times[i] = (u, v, w) will have 1 <= u, v <= N and 0 <= w <= 100.
Methodology
- Build a graph dictionary.
- Use heap to store the pair of (current step, source node). The reason why using heap is if there are two source nodes head to same target node the heap will store these two source nodes in accending order by their current step value because we store the pair in this format(current step, source node) and current step is index[0] of the pair
- Use BFS to find each source node’s target node, if the target node is not visited, we store it to visited_dictionary and if the target is visited, we continue. Then we turn these target value to source node and do the BFS again.
Code (BFS)
def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], N: int, K: int) -> int:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for u,v,w in times:
if u == v: return -1
graph[u].append((v,w))
if K not in graph: return -1
pq = [(0,K)]
dict ={}
while pq:
step, source = heapq.heappop(pq)
if source in dict: continue
dict[source]=step
for target, distance in graph[source]:
if target not in dict:
heapq.heappush(pq, (step+distance, target))
return max(dict.values()) if len(dict) == N else -1
BigO
Time Complexity: O(N^2 + E) where E is the length of times in the basic implementation, and O(ElogE) in the heap implementation, as potentially every edge gets added to the heap.