Leetcode 1145. Binary Tree Coloring Game (Python)
Related Topic
Description
Two players play a turn based game on a binary tree. We are given the root of this binary tree, and the number of nodes n in the tree. n is odd, and each node has a distinct value from 1 to n.
Initially, the first player names a value x with 1 <= x <= n, and the second player names a value y with 1 <= y <= n and y != x. The first player colors the node with value x red, and the second player colors the node with value y blue.
Then, the players take turns starting with the first player. In each turn, that player chooses a node of their color (red if player 1, blue if player 2) and colors an uncolored neighbor of the chosen node (either the left child, right child, or parent of the chosen node.)
If (and only if) a player cannot choose such a node in this way, they must pass their turn. If both players pass their turn, the game ends, and the winner is the player that colored more nodes.
You are the second player. If it is possible to choose such a y to ensure you win the game, return true. If it is not possible, return false.
Sample I/O
Example 1
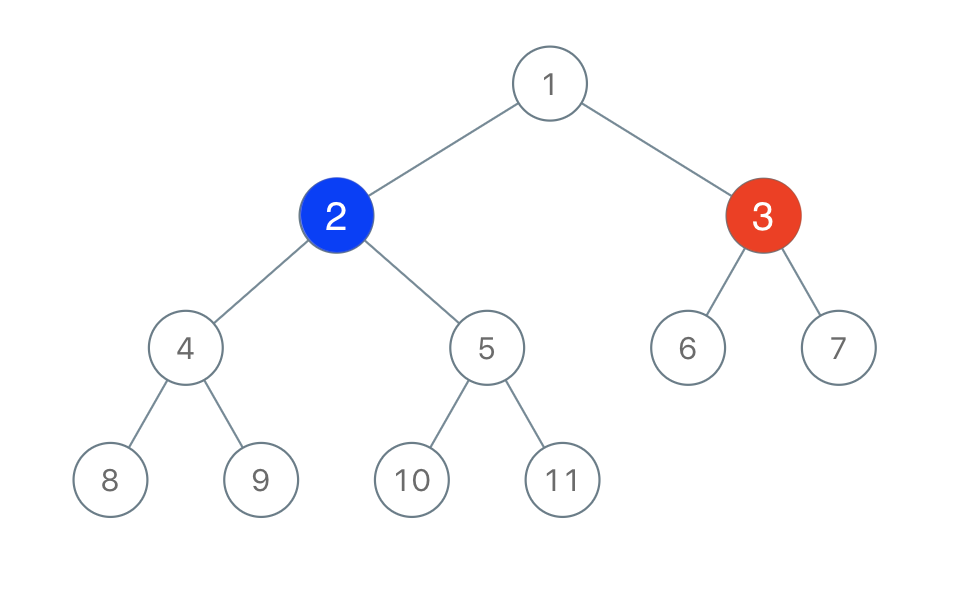
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11], n = 11, x = 3
Output: true
Explanation: The second player can choose the node with value 2.
Constraints
- root is the root of a binary tree with n nodes and distinct node values from 1 to n.
- n is odd.
- 1 <= x <= n <= 100
Methodology
Every node may has three adjacent nodes include parent node, left child node and right child node except the root node does not have parent node. To win the game, the second player need to have more than half nodes. The second player can only choose one of the three adjacent node from the first player. So we need to get the number of left subtree nodes, right subtree nodes and parent node with other node of the first player’s node. And we will sum the largest number and second largest number and compare to the total number divde by 2.
Code(DFS)
def btreeGameWinningMove(self, root: TreeNode, n: int, x: int) -> bool:
l_r_num=[0,0]
def dfs(root):
if root is None: return 0
left = dfs(root.left)
right = dfs(root.right)
if root.val == x:
l_r_num[0],l_r_num[1]=left,right
return left+right+1
total = dfs(root)
parent_num = n-sum(l_r_num)-1
return max(parent_num,max(l_r_num))>n/2
BigO
We traversal all elements of the tree once so total time complexity is O(n)