Leetcode 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node (Python)
Related Topic
Description
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Follow up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, you may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Sample I/O
Example 1
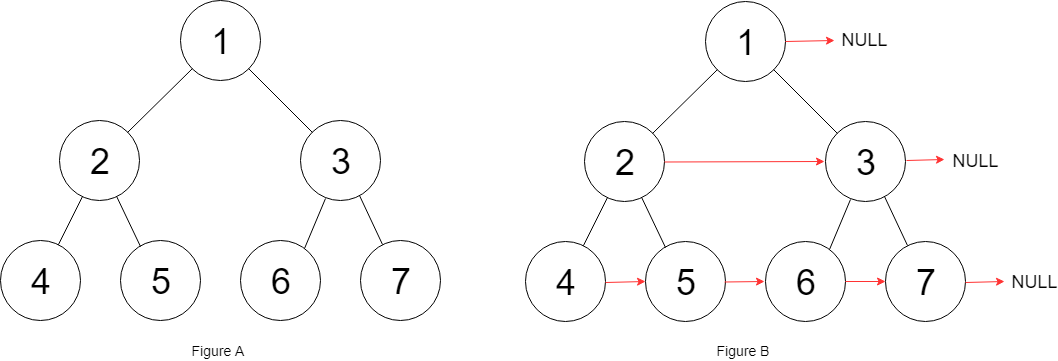
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the given tree is less than 4096.
- -1000 <= node.val <= 1000
Methodology
This question can be solved by Depth First Search
The tree is a perfect binary tree. So if there is left node then there must be right node. For each node, if it has left child node then we use next pointer to connect the left child node to right child node. If the node has next pointer, then the node’s right child node will use next pointer to connect to the node’s next node’s left child node.
Code
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val, left, right, next):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if root is None or root.left is None:
return root
root.left.next = root.right
if root.next:
root.right.next = root.next.left
self.connect(root.left)
self.connect(root.right)
return root
BigO
We traversal all nodes of the tree once so the time complexity is O(n)