Leetcode 63. Unique Paths II (Python)
Related Topic
Description
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
Sample I/O
Example 1
Input:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
Note:
m and n will be at most 100.
Methodology
This question solved by Dynamic Programming. It is similar with question 62 Unique Paths. The only difference is now the map has obstacles. We can slightly modify the code of question 62.
-
Find the base case:
Generally, there is only one way to reach the left most edge and there is only one way to reach the bottom most edge. So we init the first row and first column of 2D list with 1.
1,1,1,1,1,1,1 1,x,x,x,x,x,x 1,x,x,x,x,x,x 1,x,x,x,x,x,xBut there are two special cases involved. If there are obstacles in first row or first column.
- Obstacles in first row (for example the obstacle is at index 4):
1,1,1,1,0,0,0 1,x,x,x,x,x,x 1,x,x,x,x,x,x 1,x,x,x,x,x,x - Obstacles in first column (for example the obstacle is at index 2):
1,1,1,1,1,1,1 1,x,x,x,x,x,x 0,x,x,x,x,x,x 0,x,x,x,x,x,xOnce there is obstacle in first row or first column, then it is impossible to reach to the end of the first row or column because the robot can only move right or move down.
- Obstacles in first row (for example the obstacle is at index 4):
-
Find the pattern:
The robot can only move either down or right. For each target cell that the robot want to reach, it is either from left cell of the tagret or from up cell of the target. When the target cell is an obstacle, from target cell, the right path and down path are blocked. That means obstacle have 0 way to go down or right. After that, we need sum up target’s left cell and up cell to get the total path to reach the target cell.
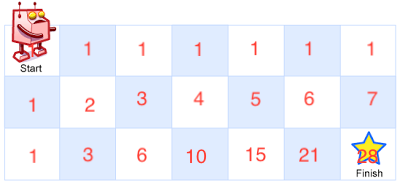
-
Answer:
When reach to the bottom-right corner, then number in the bottom-right corner will be the answer.
Code
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m = len(obstacleGrid)
n = len(obstacleGrid[0])
if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
return 0
if m<=1 or n<=1: return 0 if obstacleGrid[m-1][n-1] == 1 else 1
dp = [[0]*n for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1:
dp[i][0] = 0
break
dp[i][0] = 1
for j in range(n):
if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1:
dp[0][j] == 0
break
dp[0][j] = 1
for i in range(1,m):
for j in range(1,n):
if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
dp[i][j] = 0
else:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1]
return dp[m-1][n-1]
BigO
Init the first row and first column that will cost O(m+n). Then iterate all 2D dp array, it will cost O(m*n). In total will cost (m+n+mn), So generally, it is O(n^2)